Dive into the fascinating world of cell biology with our exclusive cell cycle and cancer worksheet PDF. This comprehensive guide unlocks the secrets of the cell cycle, its intricate checkpoints, and its profound implications in cancer development.
Explore how cancer cells manipulate these checkpoints, the role of oncogenes and tumor suppressors, and the cutting-edge cancer therapies that target the cell cycle. Embark on a journey of discovery and unravel the complex relationship between cell growth and the onset of cancer.
Cell Cycle Overview: Cell Cycle And Cancer Worksheet Pdf
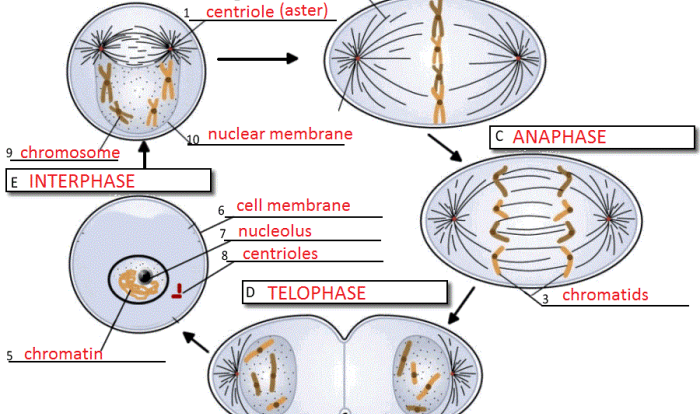
The cell cycle is the process by which a cell grows and divides. It is a continuous process that consists of four distinct phases: G1, S, G2, and M. During the G1 phase, the cell grows and prepares for DNA replication.
During the S phase, the cell’s DNA is replicated. During the G2 phase, the cell checks for DNA damage and prepares for mitosis. During the M phase, the cell divides into two new cells.
The cell cycle is regulated by a number of checkpoints. These checkpoints ensure that the cell is ready to proceed to the next phase of the cycle. If a checkpoint is not met, the cell will either stop dividing or will undergo apoptosis (programmed cell death).
Checkpoints in the Cell Cycle
There are three main checkpoints in the cell cycle: the G1 checkpoint, the S checkpoint, and the G2/M checkpoint. The G1 checkpoint occurs at the end of the G1 phase. It ensures that the cell has grown enough and has enough nutrients to proceed to the S phase.
The S checkpoint occurs at the end of the S phase. It ensures that the cell’s DNA has been replicated correctly. The G2/M checkpoint occurs at the end of the G2 phase. It ensures that the cell is ready to undergo mitosis.
Regulation of the Cell Cycle, Cell cycle and cancer worksheet pdf
The cell cycle is regulated by a number of proteins. These proteins include cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), and tumor suppressor proteins. Cyclins are proteins that activate CDKs. CDKs are enzymes that phosphorylate other proteins, which triggers the cell to proceed to the next phase of the cycle.
Tumor suppressor proteins are proteins that inhibit the cell cycle. They ensure that the cell does not divide too quickly or in an uncontrolled manner.
Cancer and the Cell Cycle
Cancer cells are characterized by uncontrolled cell division, which results from the evasion of normal cell cycle checkpoints. These checkpoints are crucial for maintaining genomic integrity and preventing the propagation of damaged cells.
Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes
Oncogenes are mutated genes that promote cell proliferation and survival. They can arise from the activation of proto-oncogenes, which are normal genes involved in cell growth and division. Tumor suppressor genes, on the other hand, inhibit cell proliferation and promote apoptosis (programmed cell death).
Mutations that inactivate tumor suppressor genes can contribute to cancer development.
Cancer Therapies Targeting the Cell Cycle
Various cancer therapies aim to disrupt the cell cycle and prevent uncontrolled cell division. These include:
- Cell Cycle Inhibitors:These drugs block specific proteins involved in cell cycle progression, such as cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) and their regulatory subunits (cyclins).
- DNA Damaging Agents:These agents induce DNA damage, which triggers cell cycle checkpoints and can lead to apoptosis if the damage is irreparable.
- Anti-Mitotic Agents:These drugs interfere with the formation of the mitotic spindle, preventing cell division.
Understanding the cell cycle and its dysregulation in cancer is crucial for developing effective cancer therapies that target specific vulnerabilities in cancer cells.
Cell Cycle and Cancer Worksheet
The Cell Cycle and Cancer Worksheet is a valuable resource for students and educators seeking to delve deeper into the intricacies of the cell cycle and its connection to cancer development. This worksheet provides a structured approach to exploring the fundamental concepts and mechanisms involved in these critical biological processes.
Understanding the Cell Cycle
The worksheet begins by introducing the cell cycle, its various stages, and the key events that occur during each phase. Students will learn about the processes of DNA replication, mitosis, and cytokinesis, and how these processes contribute to cell growth and division.
Cancer and the Cell Cycle
The worksheet then explores the connection between the cell cycle and cancer. Students will examine how disruptions in the cell cycle can lead to uncontrolled cell growth and proliferation, characteristic of cancerous cells. They will investigate the role of mutations in oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes in cancer development and learn about the different types of cancer that can arise from cell cycle dysregulation.
Using the Worksheet Effectively
To make the most of the Cell Cycle and Cancer Worksheet, it is recommended to:
- Read the introductory material carefully to gain an overview of the topic.
- Complete the worksheet questions thoroughly, referencing the provided resources and additional research materials as needed.
- Review the answers and explanations to reinforce your understanding of the concepts.
- Use the worksheet as a basis for further exploration and discussion on the cell cycle and cancer.
Worksheet Activities
The worksheet includes various activities designed to enhance students’ understanding of the cell cycle and its relationship to cancer.
These activities are organized to guide students through a structured learning journey, reinforcing key concepts and fostering critical thinking.
Activity Table
The worksheet features a comprehensive table that Artikels each activity, providing a clear overview of their objectives and procedures.
- The table includes columns for activity name, objective, materials required, and step-by-step instructions.
- This organized format allows students to quickly identify the purpose and requirements of each activity, facilitating efficient time management.
Learning Objectives
Each activity is aligned with specific learning objectives, ensuring a targeted approach to knowledge acquisition.
- The learning objectives are clearly stated at the beginning of each activity, providing students with a clear understanding of the intended outcomes.
- By aligning the activities with specific objectives, students can effectively focus their efforts and maximize their learning.
Classroom Implementation
The activities in the worksheet are designed to be adaptable to various classroom settings, allowing for flexibility in teaching approaches.
- Teachers can choose to incorporate individual activities or combine them to create a comprehensive lesson plan.
- The activities can be used as stand-alone exercises or integrated into larger discussions and projects.
- By providing a range of activities, teachers can cater to diverse learning styles and ensure engagement among all students.
FAQ Compilation
What is the significance of the cell cycle?
The cell cycle is essential for growth, development, and tissue repair. It ensures the orderly progression of cells through different stages of growth, division, and maturation.
How do cancer cells evade cell cycle checkpoints?
Cancer cells often acquire mutations that disrupt cell cycle checkpoints, allowing them to bypass normal growth controls and proliferate uncontrollably.
What is the role of oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes in cancer?
Oncogenes promote cell growth and division, while tumor suppressor genes inhibit these processes. Mutations in these genes can lead to the development of cancer.