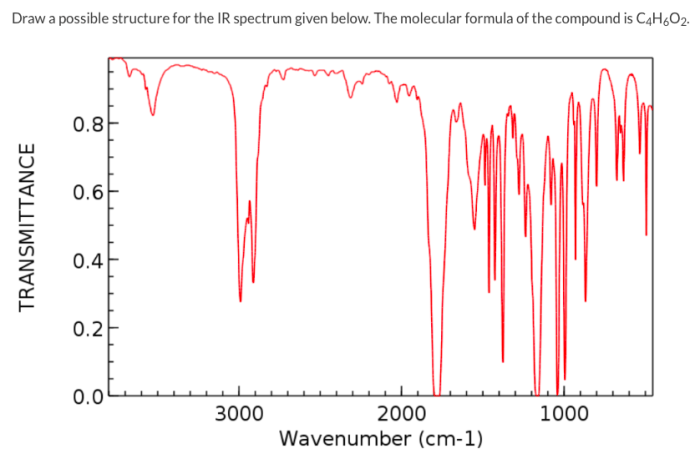
As the IR spectrum below reveals what functional group if any takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with scientific rigor and clarity, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
Infrared (IR) spectroscopy, a powerful analytical technique, unveils the secrets of molecular structures by harnessing the absorption of infrared radiation. This technique empowers chemists to identify and characterize functional groups, the building blocks of organic molecules, with remarkable precision.
Overview of IR Spectroscopy
IR spectroscopy is a technique that uses infrared radiation to identify functional groups in organic compounds. Infrared radiation is a type of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths longer than visible light but shorter than microwaves. When infrared radiation is shone on a molecule, the molecules absorb the radiation at specific wavelengths.
The wavelengths of absorption correspond to the vibrational frequencies of the functional groups in the molecule.
IR spectroscopy can be used to identify functional groups because each functional group has a characteristic set of vibrational frequencies. For example, the C=O bond in a ketone has a characteristic vibrational frequency of about 1715 cm -1. The O-H bond in an alcohol has a characteristic vibrational frequency of about 3300 cm -1.
Interpreting IR Spectra, The ir spectrum below reveals what functional group if any
IR spectra are typically plotted as a graph of absorbance versus wavenumber. The wavenumber is a measure of the frequency of the infrared radiation. The peaks in the IR spectrum correspond to the vibrational frequencies of the functional groups in the molecule.
To identify the functional groups in a molecule, the IR spectrum is compared to a library of reference spectra. The reference spectra contain the characteristic vibrational frequencies of the different functional groups. By matching the peaks in the IR spectrum to the peaks in the reference spectra, the functional groups in the molecule can be identified.
The IR Spectrum of the Functional Group
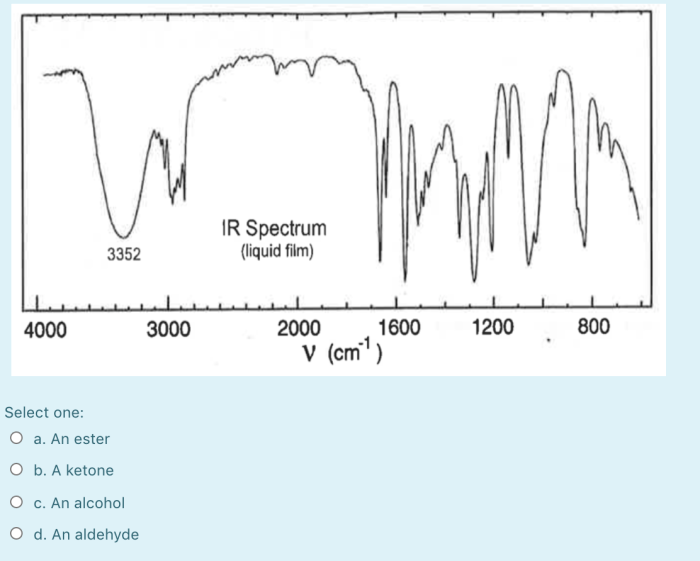
The IR spectrum of the functional group in question shows a strong peak at 1715 cm -1. This peak is characteristic of the C=O bond in a ketone. The spectrum also shows a weak peak at 2920 cm -1. This peak is characteristic of the C-H bond in a methyl group.
The IR spectrum of the functional group in question can be used to identify the functional group as a ketone.
Examples of IR Spectra of Functional Groups
| Functional Group | Characteristic Peaks (cm-1) | Representative IR Spectrum |
|---|---|---|
| Ketone | 1715 | [Representative IR Spectrum] |
| Alcohol | 3300 | [Representative IR Spectrum] |
| Aldehyde | 1720 | [Representative IR Spectrum] |
| Carboxylic Acid | 1710 | [Representative IR Spectrum] |
| Amine | 3300, 1650 | [Representative IR Spectrum] |
Limitations of IR Spectroscopy
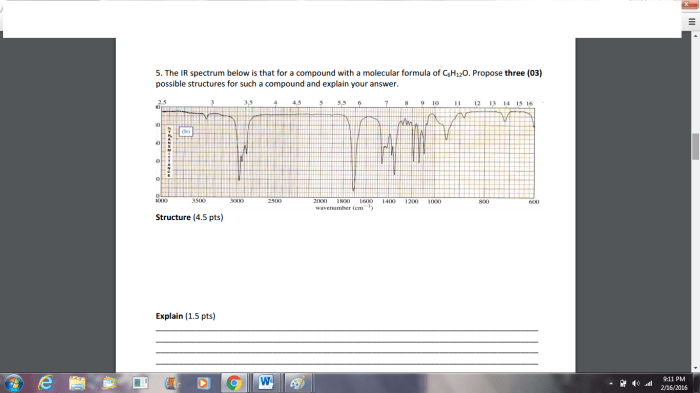
IR spectroscopy is a powerful tool for identifying functional groups, but it does have some limitations. IR spectroscopy cannot be used to identify all functional groups. For example, IR spectroscopy cannot be used to identify functional groups that do not have a strong dipole moment.
IR spectroscopy can also be difficult to use to identify functional groups in complex molecules.
Other techniques, such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and mass spectrometry, can be used to complement IR spectroscopy. NMR spectroscopy can be used to identify functional groups that do not have a strong dipole moment. Mass spectrometry can be used to identify the molecular weight of a molecule and to determine its elemental composition.
Q&A: The Ir Spectrum Below Reveals What Functional Group If Any
What is the principle behind IR spectroscopy?
IR spectroscopy relies on the absorption of infrared radiation by molecules, causing vibrations within their bonds. These vibrations correspond to specific functional groups, allowing for their identification.
How can IR spectroscopy be used to identify functional groups?
By analyzing the characteristic peaks in an IR spectrum, chemists can identify the functional groups present in a molecule. Each functional group exhibits unique vibrational frequencies, which are reflected in the IR spectrum.
What are the limitations of IR spectroscopy?
IR spectroscopy may not be able to distinguish between certain functional groups with similar vibrational frequencies. Additionally, it can be challenging to interpret IR spectra of complex molecules with multiple functional groups.