Draw the major product for the dehydration of 2-pentanol – In the realm of organic chemistry, dehydration reactions hold immense significance, enabling the transformation of alcohols into alkenes. Among these reactions, the dehydration of 2-pentanol stands out, offering a fascinating interplay of regioselectivity and stereoselectivity. This guide delves into the intricacies of this reaction, providing a comprehensive understanding of its mechanism, major product formation, and practical applications.
Dehydration of 2-Pentanol
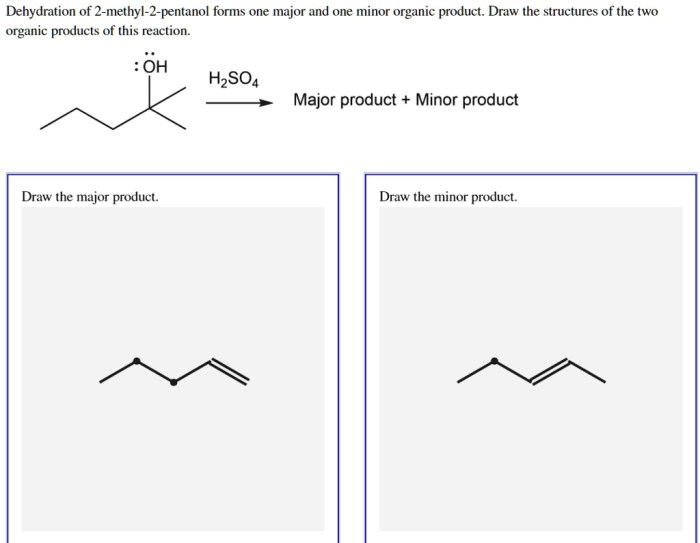
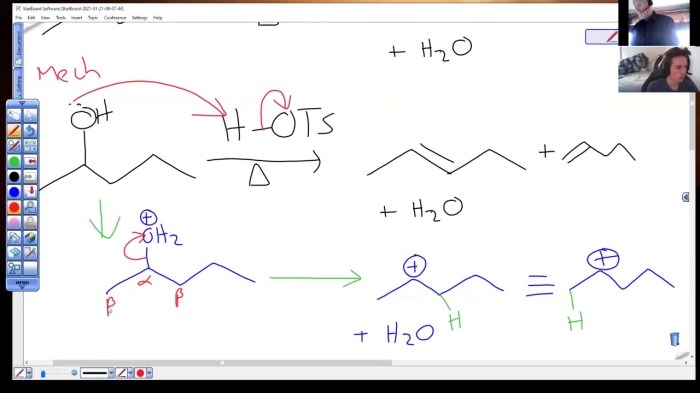
Dehydration reactions are fundamental in organic chemistry, involving the removal of water from a molecule to form a new double bond. The dehydration of 2-pentanol is a classic example of an elimination reaction.
Mechanism and Reaction Conditions, Draw the major product for the dehydration of 2-pentanol
The dehydration of 2-pentanol proceeds via an E2 elimination mechanism, where two groups (a proton and a hydroxyl group) are eliminated simultaneously in a concerted manner.
Acid catalysts, such as sulfuric acid or phosphoric acid, promote the reaction by protonating the hydroxyl group, making it a better leaving group.
Optimal reaction conditions include elevated temperatures and the use of aprotic solvents, such as dichloromethane or benzene.
Major Product Identification
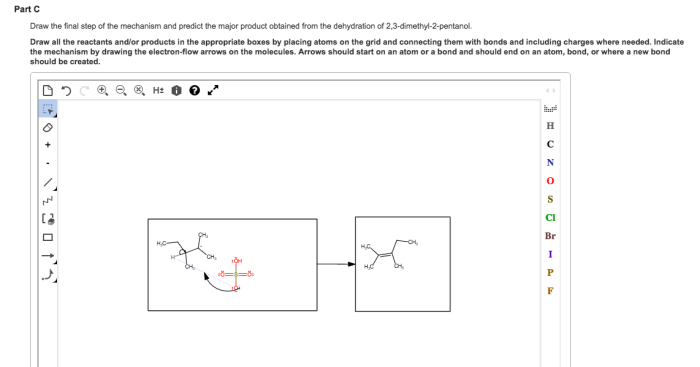
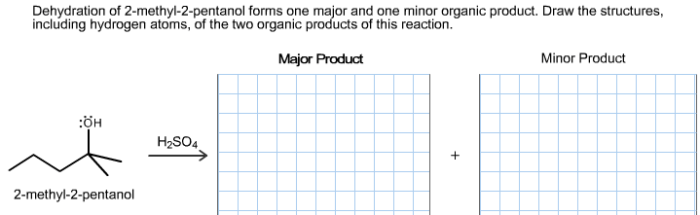
The major product of the dehydration of 2-pentanol is 2-pentene, which is formed via the removal of the proton from the more substituted carbon (the carbon adjacent to the hydroxyl group) and the hydroxyl group from the adjacent carbon.
This regioselectivity is attributed to the greater stability of the more substituted alkene, which is known as Zaitsev’s rule.
Alternative Methods and Comparisons
Alternative methods for the dehydration of alcohols include:
- Treatment with thionyl chloride (SOCl 2)
- Reaction with phosphoric acid (H 3PO 4)
Thionyl chloride offers a more efficient and rapid dehydration, while phosphoric acid is a milder reagent that can be used at lower temperatures.
Applications and Examples
The dehydration of 2-pentanol is a versatile reaction with numerous applications:
- Synthesis of 2-pentene, an important intermediate in the production of plastics and polymers
- Dehydration of other alcohols to produce alkenes
- Removal of water from organic solvents
Essential Questionnaire: Draw The Major Product For The Dehydration Of 2-pentanol
What is the major product of the dehydration of 2-pentanol?
The major product is 2-pentene, formed via the E2 elimination pathway.
Why is the E2 elimination pathway favored over the E1 pathway in the dehydration of 2-pentanol?
The E2 pathway is favored due to the presence of a strong base, which facilitates the simultaneous removal of the proton and hydroxyl group.
What factors influence the regioselectivity of the dehydration of 2-pentanol?
The regioselectivity is influenced by the stability of the carbocation formed during the reaction, with the more stable carbocation leading to the major product.