Embarking on a journey into the intricate realm of cell division, we present the cell cycle and mitosis worksheet answer key, an invaluable guide to understanding the fundamental processes that govern the life and proliferation of cells. This comprehensive resource delves into the complexities of the cell cycle, unraveling its stages and checkpoints, while shedding light on the fascinating process of mitosis, the mechanism by which cells divide and replicate their genetic material.
Overview of the Cell Cycle
The cell cycle is the series of events that occur in a cell leading to its division and duplication. It is divided into four distinct stages: interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.Interphase is the longest stage of the cell cycle and is characterized by cell growth and DNA replication.
Prophase is the stage where the chromosomes become visible and the nuclear envelope breaks down. Metaphase is the stage where the chromosomes line up in the center of the cell. Anaphase is the stage where the chromosomes are separated and pulled to opposite ends of the cell.
Telophase is the final stage of the cell cycle where the nuclear envelope reforms around the chromosomes and the cell divides into two daughter cells.The cell cycle is regulated by a series of checkpoints that ensure that the cell is ready to progress to the next stage.
These checkpoints are located at the end of each stage and monitor the cell for DNA damage or other problems. If a problem is detected, the cell will either pause its progress through the cell cycle or undergo apoptosis (cell death).
Mitosis: Cell Cycle And Mitosis Worksheet Answer Key
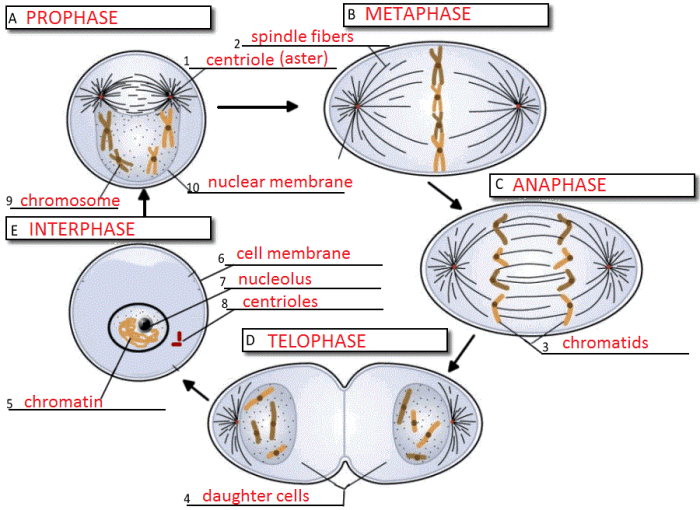
Mitosis is the process of cell division that results in two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. It is a continuous process, but for the sake of study, it can be divided into four distinct stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.Prophase
is the first stage of mitosis and is characterized by the condensation of the chromosomes and the breakdown of the nuclear envelope. Metaphase is the second stage of mitosis and is characterized by the alignment of the chromosomes in the center of the cell.
Anaphase is the third stage of mitosis and is characterized by the separation of the chromosomes and their movement to opposite ends of the cell. Telophase is the final stage of mitosis and is characterized by the formation of two new nuclear envelopes around the chromosomes and the division of the cell into two daughter cells.The
role of chromosomes in mitosis is to ensure that each daughter cell receives a complete set of genetic material. Chromosomes are made up of DNA, which contains the instructions for all of the cell’s activities. During mitosis, the chromosomes are duplicated and then separated so that each daughter cell receives one copy of each chromosome.
Worksheet Answer Key
Question 1:What is the purpose of the cell cycle? Answer:The purpose of the cell cycle is to ensure that cells grow and divide in a controlled manner. This process is essential for the growth and development of organisms and for the replacement of damaged or old cells.
Question 2:What are the four stages of mitosis? Answer:The four stages of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Question 3:What is the role of chromosomes in mitosis? Answer:The role of chromosomes in mitosis is to ensure that each daughter cell receives a complete set of genetic material.
Applications of the Cell Cycle and Mitosis
The cell cycle and mitosis are essential processes for the growth and development of organisms. They are also used in a variety of applications in medicine and cancer research.In medicine, the cell cycle is used to study the growth and spread of cancer cells.
By understanding how the cell cycle is regulated, doctors can develop new drugs and treatments to target cancer cells and prevent them from dividing.In cancer research, the cell cycle is used to study the development and progression of cancer. By understanding how the cell cycle is disrupted in cancer cells, researchers can develop new ways to prevent and treat cancer.Mitosis
is also used in biotechnology to produce genetically modified organisms (GMOs). GMOs are organisms that have had their DNA altered in a way that does not occur naturally. Mitosis is used to produce GMOs by inserting new genes into cells and then allowing the cells to divide and grow.
FAQ Insights
What is the significance of the cell cycle?
The cell cycle is crucial for maintaining tissue homeostasis, growth, and development. Dysregulation of the cell cycle can lead to various diseases, including cancer.
How many phases are there in mitosis?
Mitosis consists of four distinct phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
What is the role of chromosomes in mitosis?
Chromosomes carry the genetic material and are duplicated during the S phase of the cell cycle. During mitosis, chromosomes condense and align along the metaphase plate, ensuring equal distribution of genetic material to daughter cells.