Welcome to the realm of connective tissue matrix worksheet answers, where we embark on a journey to unravel the intricacies of this vital component of our bodies. Prepare to delve into a world of structural support, flexibility, and hydration as we explore the composition, functions, and clinical significance of the connective tissue matrix.
From its diverse components like collagen and proteoglycans to its involvement in wound healing and tissue repair, this comprehensive guide will provide you with a profound understanding of the connective tissue matrix and its indispensable role in maintaining our health and well-being.
Introduction to Connective Tissue Matrix
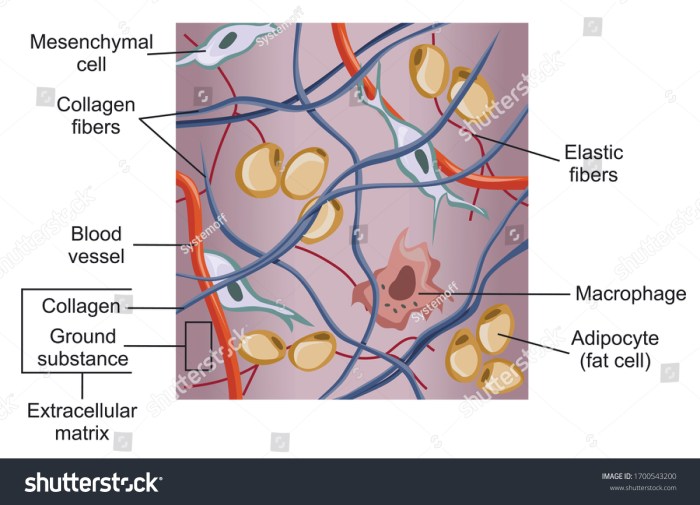
The connective tissue matrix is a complex network of extracellular components that provides structural support, flexibility, and hydration to tissues and organs. It is composed of a variety of proteins, carbohydrates, and proteoglycans that interact to create a dynamic and responsive environment.
Types of Connective Tissue Matrix
- Loose connective tissue:Found in subcutaneous tissue, around blood vessels, and in the lining of organs. Provides support and flexibility.
- Dense connective tissue:Found in tendons, ligaments, and joint capsules. Provides high tensile strength and resistance to stretching.
- Cartilage:Found in joints, ears, and the nose. Provides support, shock absorption, and flexibility.
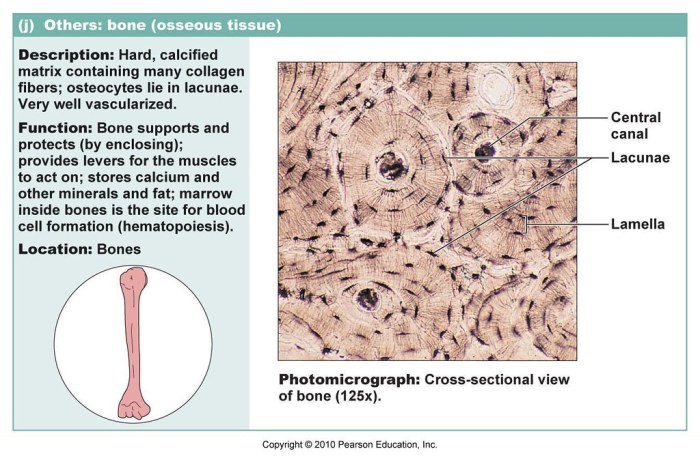
- Bone:The hardest and most rigid type of connective tissue. Provides structural support and protection.
- Blood:A fluid connective tissue that transports oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body.
Components of Connective Tissue Matrix: Connective Tissue Matrix Worksheet Answers
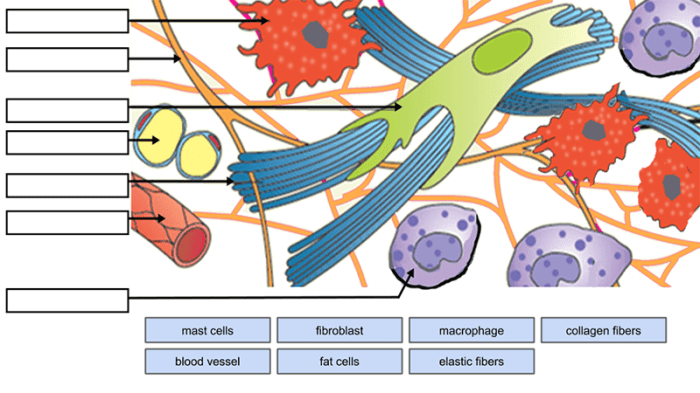
Collagen
The most abundant protein in the connective tissue matrix. Provides tensile strength and resistance to stretching.
Elastin
A flexible protein that allows tissues to stretch and recoil. Found in arteries, lungs, and skin.
Proteoglycans
Large, complex molecules that consist of a protein core surrounded by glycosaminoglycans. Provide hydration and cushioning.
Glycosaminoglycans
Long, unbranched polysaccharides that bind to water molecules. Provide hydration, lubrication, and resistance to compression.
Functions of Connective Tissue Matrix
The connective tissue matrix plays a crucial role in supporting tissues and organs and maintaining their function:
- Structural support:Provides a framework for tissues and organs, giving them shape and stability.
- Flexibility:Allows tissues to stretch and recoil, enabling movement and resilience.
- Hydration:Glycosaminoglycans bind to water molecules, providing hydration and cushioning for tissues.
- Transport:Blood, a fluid connective tissue, transports oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body.
- Wound healing:Connective tissue matrix components play a role in the formation of new tissue during wound healing.
- Immune responses:Connective tissue matrix molecules interact with immune cells to facilitate immune responses.
Clinical Significance of Connective Tissue Matrix
Disorders of the connective tissue matrix can have significant clinical implications:
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
A group of inherited disorders characterized by joint hypermobility, skin hyperextensibility, and tissue fragility.
Marfan Syndrome, Connective tissue matrix worksheet answers
An inherited disorder that affects the connective tissue of the heart, blood vessels, eyes, and skeleton.
Alterations in the connective tissue matrix can affect tissue function and overall health, leading to a range of clinical manifestations.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the primary function of the connective tissue matrix?
The connective tissue matrix provides structural support, flexibility, and hydration to tissues and organs.
Name the main components of the connective tissue matrix.
Collagen, elastin, proteoglycans, and glycosaminoglycans are the key components of the connective tissue matrix.
How does the connective tissue matrix contribute to wound healing?
The connective tissue matrix provides a scaffold for cell migration and proliferation, promoting tissue repair and wound healing.